Ever since Arduino came into being, development boards have become a very common tool among engineers trying to design various kinds of circuits. The market is flooded with development boards with all sorts of features. Any requirement you might have, there is a development board for it. You want to prototype for the Internet of Things (IoT), you have a whole set; you want industrial grade, there is a different line; so on and so forth.
Aided by the open source movement, these boards provide a backbone for electronics designers. Most of these solutions consist of connections that are pre-made and require simply adding the finishing touches. Priced as low as a ₹ 200, these boards can get you started on the way to becoming a circuit designer.

Increased availability of development boards
The availability of inexpensive development boards and the possibility of creating projects have been blessings for designers. Prakash Mohapatra, product manager, Toradex, says, “The extensive ecosystem of both hardware and software, backed by strong community support and low upfront cost, make these an ideal choice for hobbyists and academicians.”
These boards are now being used for prototyping circuits before these go into production. For hobbyists, these have come in handy. Automated plant watering systems or automated garage openers have become mainstream projects, thanks to the development boards. Plugging a cable and simply controlling the boards from a computer makes it sound so easy.
Tough competition for development.
Be it a simple garage door opener or a fire breathing robot, Arduino is what comes to mind as the design solution. Initially aimed at hobbyists, the range of Arduino boards has now become a means to test and prototype projects before going into production. It is an attractive solution for professional engineers as a low-cost method for validating a project’s design and quickly building a prototype. The availability combined with a wide variety of possible applications make it a very interesting solution for hobbyists and industrialists alike. But it is not just Arduino that is making a name for itself.
Most companies that have launched microcontrollers in the past decade have seen development support as vital—continuing a trend to support low-volume users. In some cases, microcontroller and software vendors have Arduino as a target for their own product development.
Of late, many new boards have entered the market. For engineers looking to try development, Tivaware from Texas Instruments is a lucrative option. It is compatible with Code Composer and Energia that give a hands-on experience for academicians looking to enter development professionally.
Curiosity boards from Microchip are also an interesting addition. Based on PIC32 microcontroller, these allow for the IoT and connectivity application development.
Mbed initiative from ARM is another option for programmers. It provides an ecosystem for the development of IoT devices, so that part-time developers can join the race.
And, if things were not diversified enough, developers have successfully added JavaScript and .Net platforms to the mainstream environment of C and C++ for usage in development boards to allow software aficionados to enter the game.
Ever since the launch of Raspberry Pi, the definition of computing has changed radically. Tinkerers have started using Raspberry Pi to make robots, data accumulators, phones and desktop computers. Applications are only limited by one’s imagination.
BeagleBoard is another popular board for engineers who like working on Linux. The top-of-the-line board consists of 2GB DDR3 RAM and 4GB 8-bit e-MMC onboard flash memory. With 3xUSB 3.0, eSATA, HDMI and 2xEthernet, it is a serious contender for top performance in development boards.
This board finds a strong contender in UDOO X86 Ultra, which sports a quad-core Intel N3710 SoC clocked at 2.56GHz. Icing on the cake is Intel HD 405 graphics on board, which are supported by 8GB DDR3 RAM. Come to think of it, my PC has got poorer configuration, much poorer!

An increasing number of interface options
A lot of development boards come with a multitude of interface options ranging from the very popular USB to technical ports like RS232. T. Anand, technical architect, Knewron, says, “Interfaces like MOD-BUS, RS232 or peripheral component interconnect (PCI) slots still exist and could be prominently seen on industrial boards, while general-purpose boards usually have USB interfaces.”
Arduino, for example, offers Registered Jack 45 (RJ45) and USB 2.0, among others, for connecting and loading programs from a computer. Most ARM based devices include a Joint Test Action Group (JTAG) interface. This can be used to program on-chip or external flash, or load directly into RAM. The JTAG is also the interface for on-chip debug and trace features. Wireless is also being used as one of the interfaces.
The post Increasing Processing Power of DIY and Hobbyist Development Boards appeared first on Electronics For You.















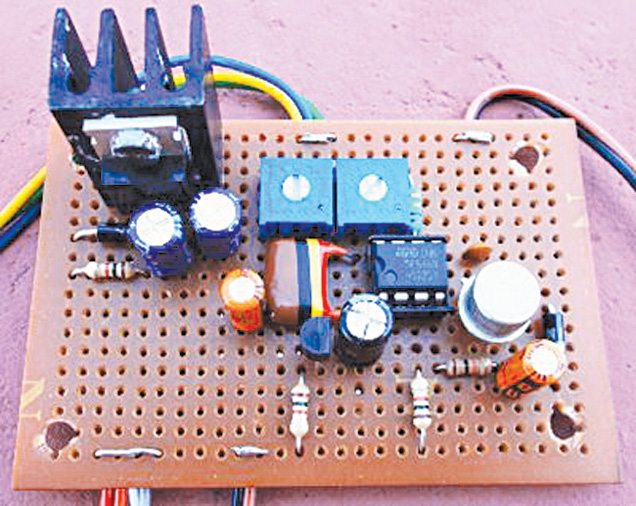
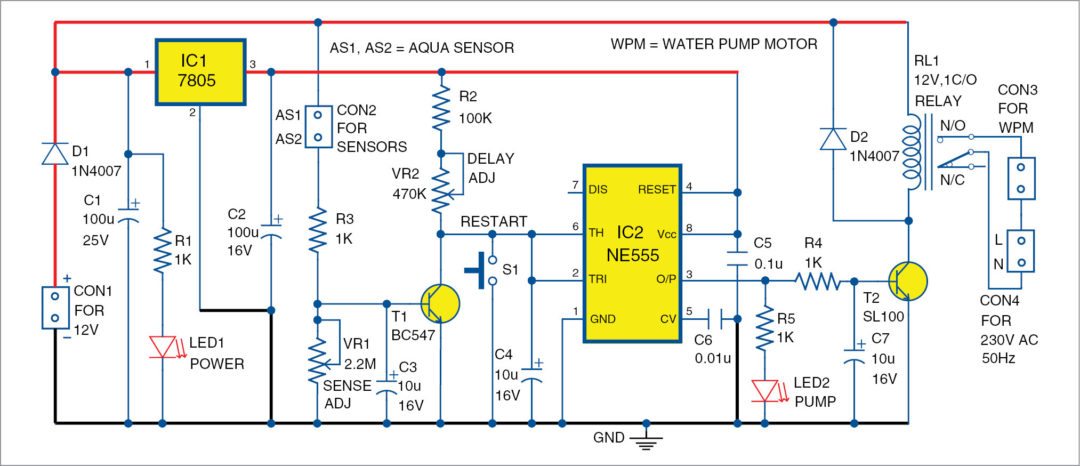
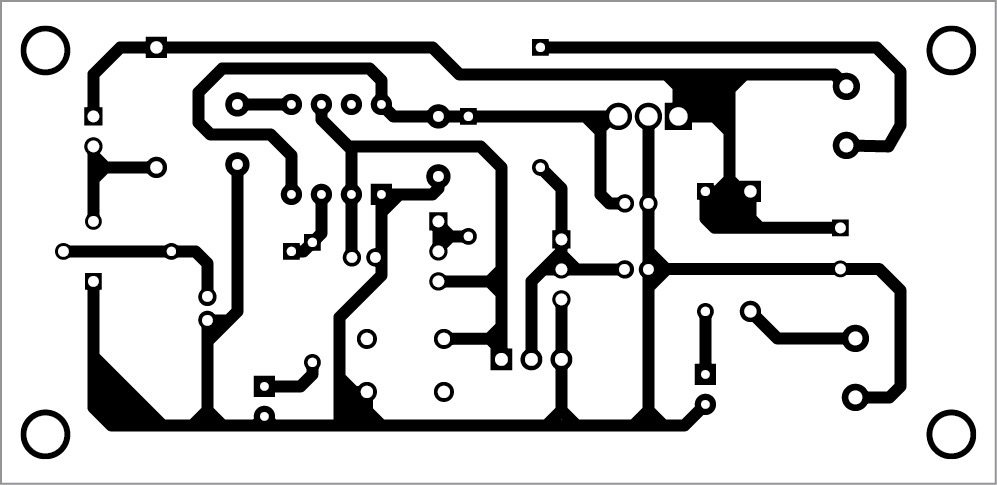
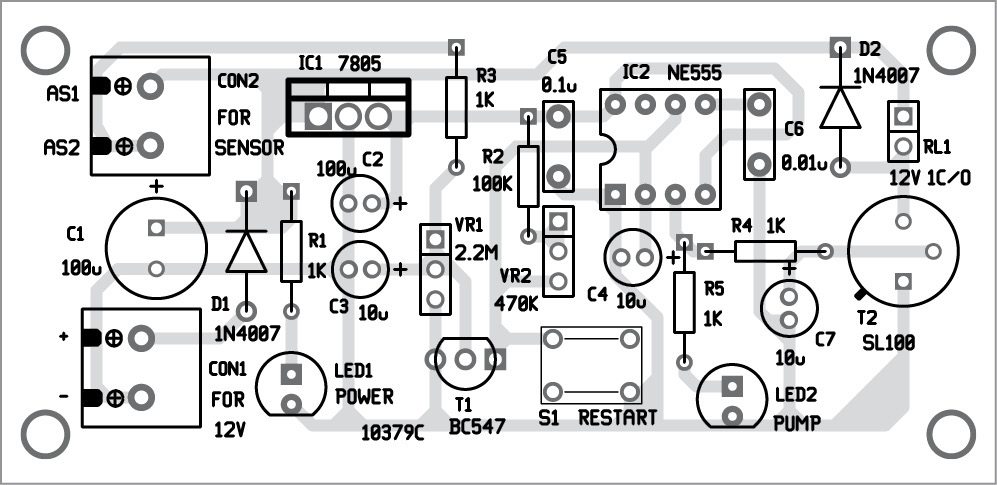
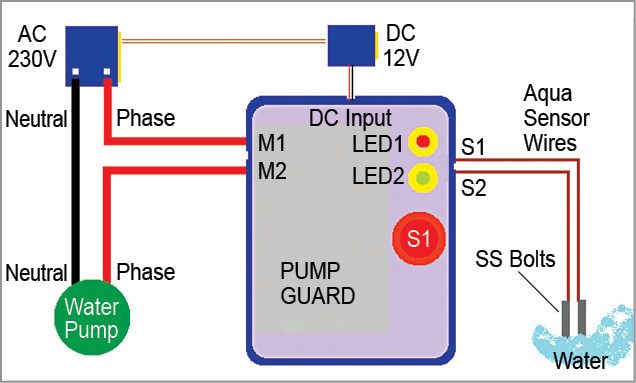
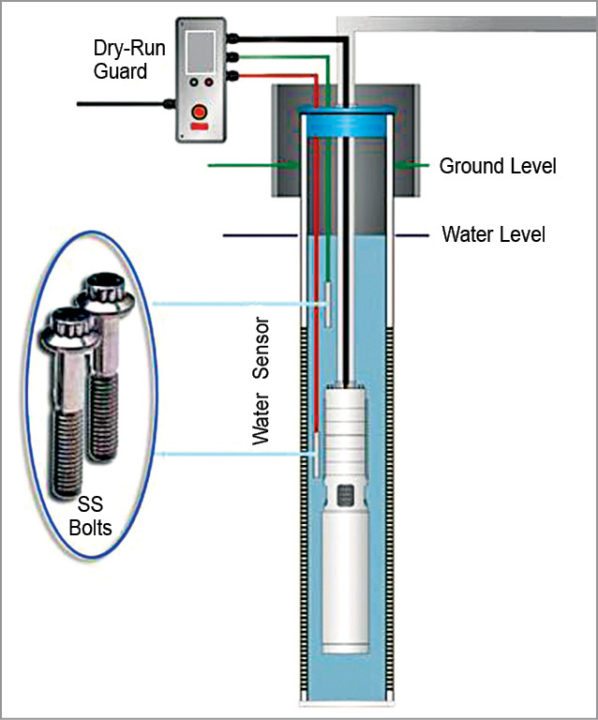
 Here is an effective solution for protection of household submersible water pumps against dry running. Minimum water-level monitoring feature in the circuit is realised using suspended sensor probes to ensure that the water pumps will not run under a dry condition. Besides, switch-on and return-delay features prevent the pumps from unwanted brief operation when handling turbulent underground water. Fig. 1 shows the author’s prototype.
Here is an effective solution for protection of household submersible water pumps against dry running. Minimum water-level monitoring feature in the circuit is realised using suspended sensor probes to ensure that the water pumps will not run under a dry condition. Besides, switch-on and return-delay features prevent the pumps from unwanted brief operation when handling turbulent underground water. Fig. 1 shows the author’s prototype.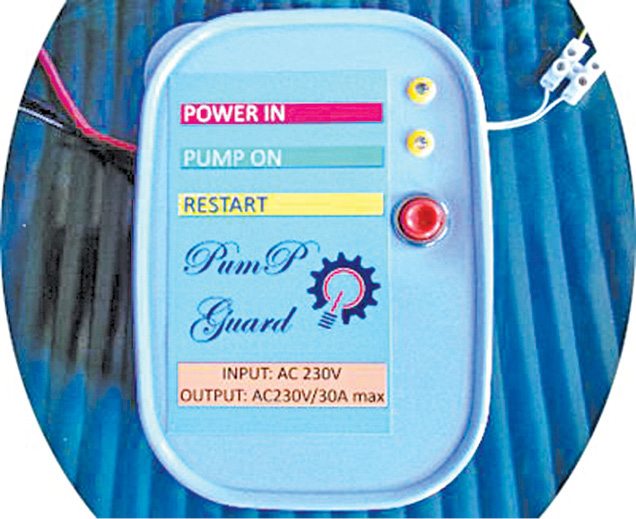







 Over 100,000 internet-connected security cameras contain a “massive” security vulnerability that allows them to be accessed via the open web and used for surveillance, roped into a malicious botnet, or even exploited to hijack other devices on the same network.
Over 100,000 internet-connected security cameras contain a “massive” security vulnerability that allows them to be accessed via the open web and used for surveillance, roped into a malicious botnet, or even exploited to hijack other devices on the same network. Cybersecurity isn’t exactly new, but it’s becoming one of the hottest areas on the startup scene.With global malware attacks like WannaCry garnering widespread attention and press coverage, and companies and consumers growing increasingly worried about how security threats are rapidly evolving and diversifying, investors and entrepreneurs alike are seeing big opportunities.
Cybersecurity isn’t exactly new, but it’s becoming one of the hottest areas on the startup scene.With global malware attacks like WannaCry garnering widespread attention and press coverage, and companies and consumers growing increasingly worried about how security threats are rapidly evolving and diversifying, investors and entrepreneurs alike are seeing big opportunities. Any doubt that Internet of Things (IoT) devices have the ability to wreak digital havoc was removed during the last quarter of 2016 when IoT-device powered Mirai botnets handily disrupted internet service.
Any doubt that Internet of Things (IoT) devices have the ability to wreak digital havoc was removed during the last quarter of 2016 when IoT-device powered Mirai botnets handily disrupted internet service.
 It all starts with one question: Why are security officers hesitant to let go of their security appliances and move on to software or cloud-based offerings? There could be many answers to this question, but the fact is that these appliances largely live up to their namesake, i.e., emulate an overall feeling of security. CISOs don’t need to grapple with system managed devices, they have full control over their appliances, and there’s no need to report back.
It all starts with one question: Why are security officers hesitant to let go of their security appliances and move on to software or cloud-based offerings? There could be many answers to this question, but the fact is that these appliances largely live up to their namesake, i.e., emulate an overall feeling of security. CISOs don’t need to grapple with system managed devices, they have full control over their appliances, and there’s no need to report back. Although for many of us IoT presents an exciting new horizon to explore, this relatively new tech sector also opens up a great opportunity for hackers to wield their axe of destruction. While most computers and mobile devices now come with at least basic protocols and add-ons aimed at protecting us from exploits, billions of new IoT devices come into our lives without even basic means of protection.
Although for many of us IoT presents an exciting new horizon to explore, this relatively new tech sector also opens up a great opportunity for hackers to wield their axe of destruction. While most computers and mobile devices now come with at least basic protocols and add-ons aimed at protecting us from exploits, billions of new IoT devices come into our lives without even basic means of protection.