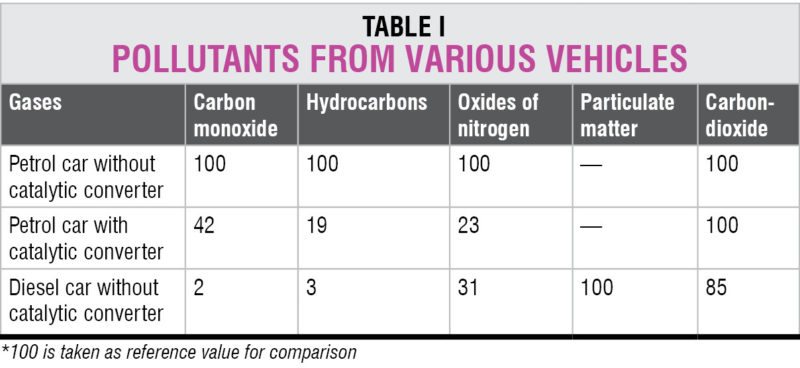
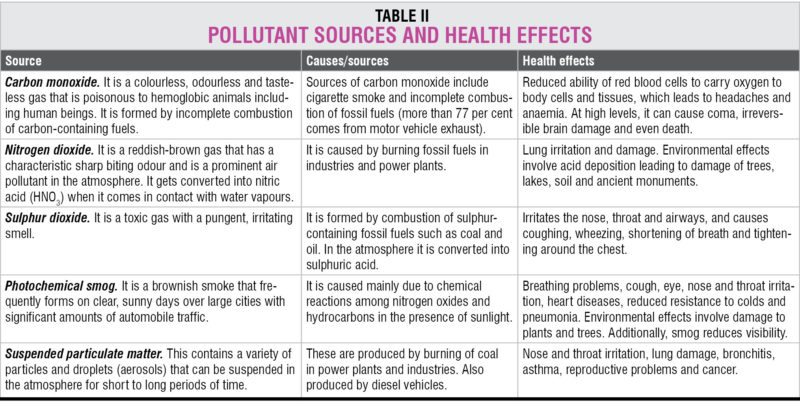
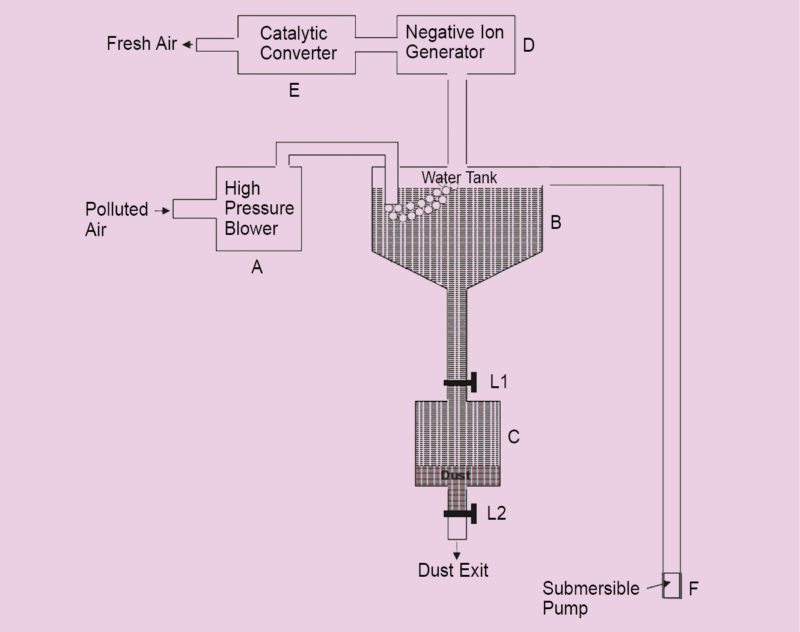
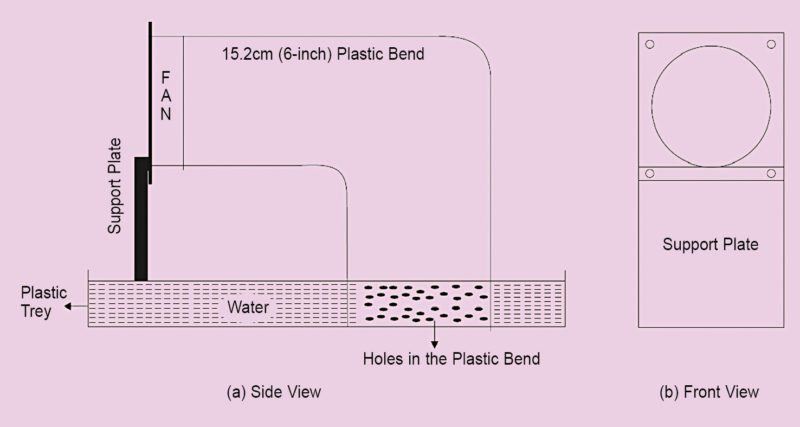
NDIA, Bangalore – July 13, 2017 – NI (Nasdaq: NATI), the provider of platform-based systems that enable engineers and scientists to solve the world’s greatest engineering challenges, announced a baseband model of the second-generation Vector Signal Transceiver (VST). The PXIe-5820 module is the industry’s first baseband VST with 1 GHz of complex I/Q bandwidth and is designed to address the most challenging RF front-end module and transceiver test applications, such as envelope tracking, digital pre-distortion and 5G test.
“In 2016, NI disrupted the industry by introducing the RF model of our second-generation VST with 1 GHz of instantaneous bandwidth,” said Charles Schroeder, vice president of RF and wireless at NI. “We’re continuing the disruption with the baseband model of our second-generation VST. Engineers can use the baseband VST with LabVIEW system design software to address the evolving and changing needs of transceiver test applications.
Engineers can take advantage of the software-designed architecture of NI’s VSTs to help accelerate the pace of design, reduce the cost of test and solve measurement problems previously unsolvable through traditional test approaches.”
The PXIe-5820 combines a wideband I/Q digitizer, wideband I/Q arbitrary waveform generator and high-performance user-programmable FPGA into a single 2-slot PXI Express module. With 1 GHz of complex I/Q bandwidth, the baseband VST suits a wide range of applications including baseband I/Q testing of wireless and cellular chipsets as well as envelope tracking of digitally pre-distorted waveforms for power amplifier, and generation and analysis of new wireless standards such as 5G, 802.11ax and LTE-Advanced Pro.
The PXIe-5820 combines a wideband I/Q digitizer, wideband I/Q arbitrary waveform generator and high-performance user-programmable FPGA into a single 2-slot PXI Express module. With 1 GHz of complex I/Q bandwidth, the baseband VST suits a wide range of applications including baseband I/Q testing of wireless and cellular chipsets as well as envelope tracking of digitally pre-distorted waveforms for power amplifier, and generation and analysis of new wireless standards such as 5G, 802.11ax and LTE-Advanced Pro.

Product Features:
· 1 GHz of complex I/Q instantaneous bandwidth for generation and analysis
· Measurement accuracy to measure 802.11ax error vector magnitude (EVM) performance of -54 dB
· Baseband 2-channel differential I/Q with 4 Vpp differential input and 2 Vpp differential output swing
· FPGA-based measurement acceleration for measurements up to 10X faster and highly optimized measurement software
· Compact size and tight synchronization of baseband and RF VSTs allowing for 2×2, 4×4, 8×8 or higher multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) configurations in the PXI form factor
· Excellent noise floor and spurious free dynamic range
· User-programmable FPGA that engineers can customize to add application-specific functionality
· Ease of programming with consistent software experience between RF and baseband VSTs
“The baseband VST is a deliberate evolution of our original software-designed architecture,” said Ruan Lourens, chief architect of R&D, RF at NI. “We have managed to optimize in every possible domain, from thermal and electrical to digital signal processing, to successfully deliver 1 GHz complex I/Q bandwidth in a small form factor. The baseband VST can be tightly synchronized with the PXIe-5840 RF VST to sub-nanosecond accuracy, to offer a complete solution for RF and baseband differential I/Q testing of wireless chipsets.”
The baseband VST is a vital part of the NI platform and ecosystem that engineers can use to build smarter test systems. These test systems benefit from more than 600 PXI products ranging from DC to mmWave. They feature high-throughput data movement using PCI Express Gen 3 bus interfaces and sub-nanosecond synchronization with integrated timing and triggering. Users can take advantage of the productivity of the LabVIEW and TestStand software environments, along with a vibrant ecosystem of partners, add-on IP and applications engineers, to help dramatically lower the cost of test, reduce time to market and future-proof testers for tomorrow’s challenging requirements.
The post Baseband Vector Signal Transceiver With 12X Bandwidth, 50 Per Cent smaller footprint and a Larger user-programmable FPGA appeared first on Electronics For You.

 This article shows you how to build a small radio station at home and share music with others. The station can also be used for making announcements in colleges, industries, hospitals, schools and other places using a condenser mic amplifier circuit.
This article shows you how to build a small radio station at home and share music with others. The station can also be used for making announcements in colleges, industries, hospitals, schools and other places using a condenser mic amplifier circuit.









 The biggest nightmare for any IoT provider is the attacks, which can effectively eradicate trust in the products or services of the company responsible for the compromised device. Relying on users to protect themselves with stronger, more complex passwords isn’t going to cut it. Numerous studies have shown that users continue to use weak passwords, even while acknowledging the associated risks.
The biggest nightmare for any IoT provider is the attacks, which can effectively eradicate trust in the products or services of the company responsible for the compromised device. Relying on users to protect themselves with stronger, more complex passwords isn’t going to cut it. Numerous studies have shown that users continue to use weak passwords, even while acknowledging the associated risks. Researchers are finding a plethora of security risks as more devices become connected to the Internet. In a recent report by Kaspersky Lab, the research company found that the number of new IoT malware samples this year has already doubled that of last year.
Researchers are finding a plethora of security risks as more devices become connected to the Internet. In a recent report by Kaspersky Lab, the research company found that the number of new IoT malware samples this year has already doubled that of last year. An incident involving a bank’s online banking services could cost the organisation $1,754,000 (about ₹11.31 crore), a report by cybersecurity firm Kaspersky has found.
An incident involving a bank’s online banking services could cost the organisation $1,754,000 (about ₹11.31 crore), a report by cybersecurity firm Kaspersky has found. New security technology that could stop cyber-attacks and protect the privacy of billions of smart device users worldwide could soon be available as a result of a partnership between the University of Kent and University of Essex.
New security technology that could stop cyber-attacks and protect the privacy of billions of smart device users worldwide could soon be available as a result of a partnership between the University of Kent and University of Essex. U.S. intelligence agencies have turned up the heat in recent days on Kaspersky Lab, the Moscow-based cybersecurity giant long suspected of ties to Russia’s spying apparatus. Now, official Kremlin documents reviewed by McClatchy could further inflame the debate about whether the company’s relationship with Russian Intelligence is more than rumor. The documents are certifications issued to the company by the Russian Security Service, the spy agency known as the FSB. Unlike the stamped approvals the FSB routinely issues to companies seeking to operate in Russia, Kaspersky’s include an unusual feature: a military intelligence unit number matching that of an FSB program.
U.S. intelligence agencies have turned up the heat in recent days on Kaspersky Lab, the Moscow-based cybersecurity giant long suspected of ties to Russia’s spying apparatus. Now, official Kremlin documents reviewed by McClatchy could further inflame the debate about whether the company’s relationship with Russian Intelligence is more than rumor. The documents are certifications issued to the company by the Russian Security Service, the spy agency known as the FSB. Unlike the stamped approvals the FSB routinely issues to companies seeking to operate in Russia, Kaspersky’s include an unusual feature: a military intelligence unit number matching that of an FSB program. While the IoT affords many advantages by connecting the world, security risks pertaining to IoT are growing and rapidly evolving. A recent report by Samsung shows that there is a need to safeguard every device by 2020. Samsung’s ‘Open Economy’ document argues, “There is a very clear danger that technology is running ahead of the game.” The complications involved with hundreds of detectors constantly collecting data within a single institution create innumerable complexities and technical challenges.
While the IoT affords many advantages by connecting the world, security risks pertaining to IoT are growing and rapidly evolving. A recent report by Samsung shows that there is a need to safeguard every device by 2020. Samsung’s ‘Open Economy’ document argues, “There is a very clear danger that technology is running ahead of the game.” The complications involved with hundreds of detectors constantly collecting data within a single institution create innumerable complexities and technical challenges. A. IEEE P1931.1 is a federated net-working and computational paradigm for the Internet of Things (IoT). It is always available for real-time on-site operation facilitation including next-hop connectiv-ity for Things (IoT products), real-time context building and decision triggers. It provides efficient data connectivity to Cloud/service providers and always-‘on’ security for Things under Roof.
A. IEEE P1931.1 is a federated net-working and computational paradigm for the Internet of Things (IoT). It is always available for real-time on-site operation facilitation including next-hop connectiv-ity for Things (IoT products), real-time context building and decision triggers. It provides efficient data connectivity to Cloud/service providers and always-‘on’ security for Things under Roof. Recognising the complexity of cyber attacks and the multi-stakeholder nature of tackling cyber security are the key components of a new data-driven cyber security system being developed by experts led by the University of Nottingham.
Recognising the complexity of cyber attacks and the multi-stakeholder nature of tackling cyber security are the key components of a new data-driven cyber security system being developed by experts led by the University of Nottingham. Now we might have to worry the Central Intelligence Agency is spying on us through our Samsung television set, intercepting text messages, and using the phone’s camera to secretly photograph me.
Now we might have to worry the Central Intelligence Agency is spying on us through our Samsung television set, intercepting text messages, and using the phone’s camera to secretly photograph me. On the heels of the most recent worldwide ransomware attack, it is more important than ever for companies with critical infrastructure and IoT devices to secure their environments.
On the heels of the most recent worldwide ransomware attack, it is more important than ever for companies with critical infrastructure and IoT devices to secure their environments. When You Think
When You Think  The Air Force is now operationalizing several key elements in its comprehensive cybersecurity plan, designed to analyze and mitigate attacks while also building cyber resilience into new weapons systems and platforms early in the acquisition process, service leaders said.
The Air Force is now operationalizing several key elements in its comprehensive cybersecurity plan, designed to analyze and mitigate attacks while also building cyber resilience into new weapons systems and platforms early in the acquisition process, service leaders said. Everything is now connected via the Internet of Things (IoT), and for the most part, the out-of-the-box security embedded into them is weak, and easily hacked. This potentially allows hackers to exploit devices like Amazon’s Echo, as well as the Google Home device. By accessing a connected toy, for example, the ethical hackers used in the study were able to send commands to Amazon Echo – like voice purchasing. These devices, or similar devices, will eventually be used for the maintenance and security of the home.
Everything is now connected via the Internet of Things (IoT), and for the most part, the out-of-the-box security embedded into them is weak, and easily hacked. This potentially allows hackers to exploit devices like Amazon’s Echo, as well as the Google Home device. By accessing a connected toy, for example, the ethical hackers used in the study were able to send commands to Amazon Echo – like voice purchasing. These devices, or similar devices, will eventually be used for the maintenance and security of the home.
 Device Authority, a global leader in Identity and Access Management (IAM) for the Internet of Things (IoT), today announces the latest update of its IoT security platform. One of the first products to deliver password management and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) certificates to devices without human intervention, KeyScaler™ version 5.5 is set to dramatically streamline and strengthen the ways in which organizations secure their connected devices.
Device Authority, a global leader in Identity and Access Management (IAM) for the Internet of Things (IoT), today announces the latest update of its IoT security platform. One of the first products to deliver password management and Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) certificates to devices without human intervention, KeyScaler™ version 5.5 is set to dramatically streamline and strengthen the ways in which organizations secure their connected devices. One of the NSA’s beyond–top secret hacking tools has been stolen and while the ensuing damage falls far short of an unauthorized nuclear strike, the thieves have wreaked cybermayhem around the world.
One of the NSA’s beyond–top secret hacking tools has been stolen and while the ensuing damage falls far short of an unauthorized nuclear strike, the thieves have wreaked cybermayhem around the world. World-class organizations recognize that cybersecurity can, and should, be a powerful enabler for business: they align their cybersecurity strategy with corporate strategy, they support it with the right culture and technology, they accurately measure its performance, and they understand that performance in terms of business value and return on investment.
World-class organizations recognize that cybersecurity can, and should, be a powerful enabler for business: they align their cybersecurity strategy with corporate strategy, they support it with the right culture and technology, they accurately measure its performance, and they understand that performance in terms of business value and return on investment. Security is too important to be an afterthought. No one wants to cobble together an aftermarket fix, and having to do so would not reflect well on your brand. While it is (relatively) easy to design and ship an IP camera, for example, the ease at which one can be hacked from factory settings makes installing one an unacceptable risk factor to the network – and your customer’s business.
Security is too important to be an afterthought. No one wants to cobble together an aftermarket fix, and having to do so would not reflect well on your brand. While it is (relatively) easy to design and ship an IP camera, for example, the ease at which one can be hacked from factory settings makes installing one an unacceptable risk factor to the network – and your customer’s business. IoT device designs are usually powered by microcontrollers, are less powerful and lack hardware security features compared to microprocessors. But they are well suited to IoT devices because applications do not require the computational capability of microprocessors, they consume much less power, and they cost a fraction of a microprocessor.
IoT device designs are usually powered by microcontrollers, are less powerful and lack hardware security features compared to microprocessors. But they are well suited to IoT devices because applications do not require the computational capability of microprocessors, they consume much less power, and they cost a fraction of a microprocessor. Only about half of all countries have a cybersecurity strategy or are in the process of developing one, and even the world’s most powerful countries show major gaps in their preparedness for cyberattacks, according to a latest UN report released on Wednesday.
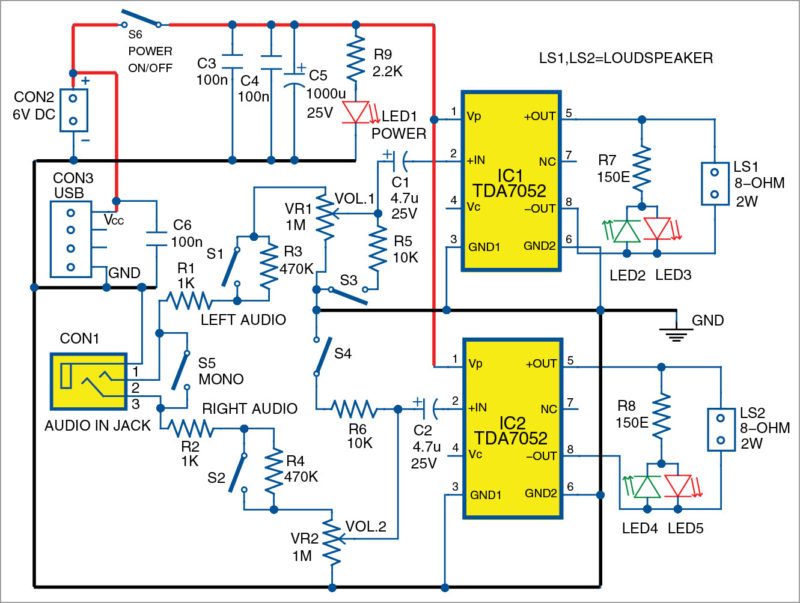
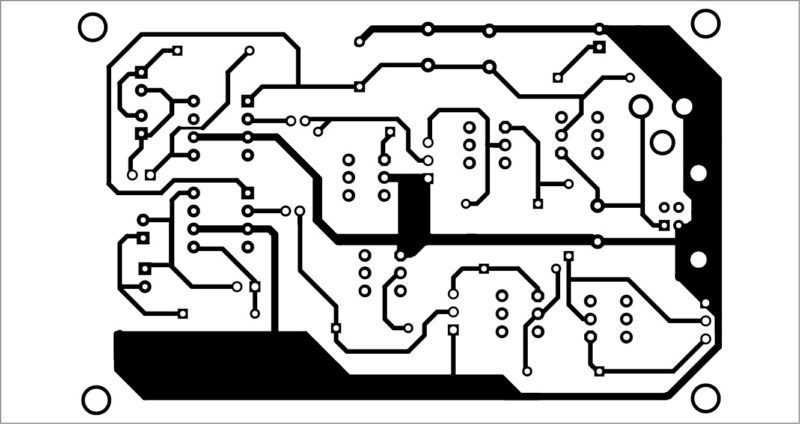
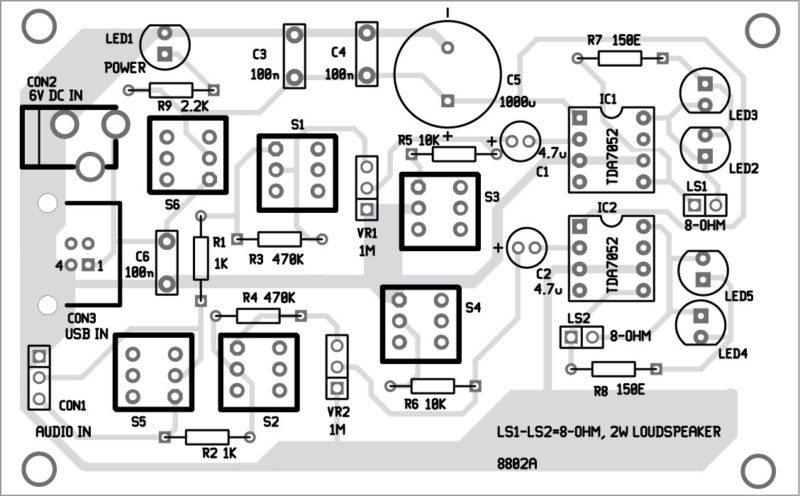
Only about half of all countries have a cybersecurity strategy or are in the process of developing one, and even the world’s most powerful countries show major gaps in their preparedness for cyberattacks, according to a latest UN report released on Wednesday. Portable devices like personal computers, MP3 players, sound recorders, telephones and audible sensors are frequently in need of additional stereo amplifier to produce sufficient sound. These audio amplifiers should work with batteries (4.5V, 6V, 12V, etc) and USB interfaces (+5V). These should have low quiescent current and produce at least 2×0.5W of output power. This output power is enough for listening in a small room with several people.
Portable devices like personal computers, MP3 players, sound recorders, telephones and audible sensors are frequently in need of additional stereo amplifier to produce sufficient sound. These audio amplifiers should work with batteries (4.5V, 6V, 12V, etc) and USB interfaces (+5V). These should have low quiescent current and produce at least 2×0.5W of output power. This output power is enough for listening in a small room with several people.


 Popular IoT home security device could allow hackers to turn burglar alarms on and off and switch on siren, says researcher who dissected it.Security researchers have discovered a number of vulnerabilities in an internet-enabled burglar alarm that could see the device being remotely switched off by an attacker.According to a blog post, Ilia Shnaidman, head of security research at Bullguard, said that the discovery of multiple flaws in iSmartAlarm is another example of a poorly engineered device that offers attackers an easy target.
Popular IoT home security device could allow hackers to turn burglar alarms on and off and switch on siren, says researcher who dissected it.Security researchers have discovered a number of vulnerabilities in an internet-enabled burglar alarm that could see the device being remotely switched off by an attacker.According to a blog post, Ilia Shnaidman, head of security research at Bullguard, said that the discovery of multiple flaws in iSmartAlarm is another example of a poorly engineered device that offers attackers an easy target.